Course
Introduction
C "Hello, World!" ProgramPrint an Integer (Entered by the User)Add Two IntegersMultiply Two Floating-Point NumbersFind ASCII Value of a CharacterCompute Quotient and RemainderFind the Size of int, float, double and charSwap Two NumbersDecision Making and Loops
Check Whether a Number is Even or OddCheck Whether a Character is a Vowel or ConsonantFind the Largest Number Among Three NumbersFind the Roots of a Quadratic EquationCheck Leap YearCheck Whether a Number is Positive or NegativeCheck Whether a Character is an Alphabet or notCalculate the Sum of Natural NumbersFind Factorial of a NumberGenerate Multiplication TableDisplay Fibonacci SequenceFind GCD of two NumbersFind LCM of two NumbersDisplay Characters from A to Z Using LoopCount Number of Digits in an IntegerReverse a NumberCalculate the Power of a NumberCheck Whether a Number is Palindrome or NotCheck Whether a Number is Prime or NotDisplay Prime Numbers Between Two IntervalsCheck Armstrong NumberDisplay Armstrong Number Between Two IntervalsDisplay Factors of a NumberMake a Simple Calculator Using switch...casePrint Pyramids and PatternsFunctions
Demonstrate the Working of Keyword longDisplay Prime Numbers Between Intervals Using FunctionCheck Prime or Armstrong Number Using User-defined FunctionCheck Whether a Number can be Expressed as Sum of Two Prime NumbersFind the Sum of Natural Numbers using RecursionFind Factorial of a Number Using RecursionFind G.C.D Using RecursionConvert Binary Number to Decimal and vice-versaConvert Octal Number to Decimal and vice-versaConvert Binary Number to Octal and vice-versaReverse a Sentence Using Recursioncalculate the power using recursionArrays and Pointers
Calculate Average Using ArraysFind Largest Element in an ArrayCalculate Standard DeviationAdd Two Matrices Using Multi-dimensional ArraysMultiply Two Matrices Using Multi-dimensional ArraysFind Transpose of a MatrixMultiply two Matrices by Passing Matrix to a FunctionAccess Array Elements Using PointerC Program Swap Numbers in Cyclic Order Using Call by ReferenceFind Largest Number Using Dynamic Memory AllocationStrings
Find the Frequency of Characters in a StringCount the Number of Vowels, Consonants and so onRemove all Characters in a String Except AlphabetsFind the Length of a StringConcatenate Two StringsCopy String Without Using strcpy()Sort Elements in Lexicographical Order (Dictionary Order)Structures and Unions
Store Information of a Student Using StructureAdd Two Distances (in inch-feet system) using StructuresAdd Two Complex Numbers by Passing Structure to a FunctionCalculate Difference Between Two Time PeriodsStore Information of Students Using StructureStore Data in Structures DynamicallyC++ Program to Find All Roots of a Quadratic Equation
To understand this example, you should have the knowledge of the following C++ programming topics:
For a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c = 0 (where a, b and c are coefficients), it’s roots is given by following the formula.

Formula to Find Roots of Quadratic Equation
The term b2-4ac is known as the discriminant of a quadratic equation. The discriminant tells the nature of the roots.
- If discriminant is greater than 0, the roots are real and different.
- If discriminant is equal to 0, the roots are real and equal.
- If discriminant is less than 0, the roots are complex and different.
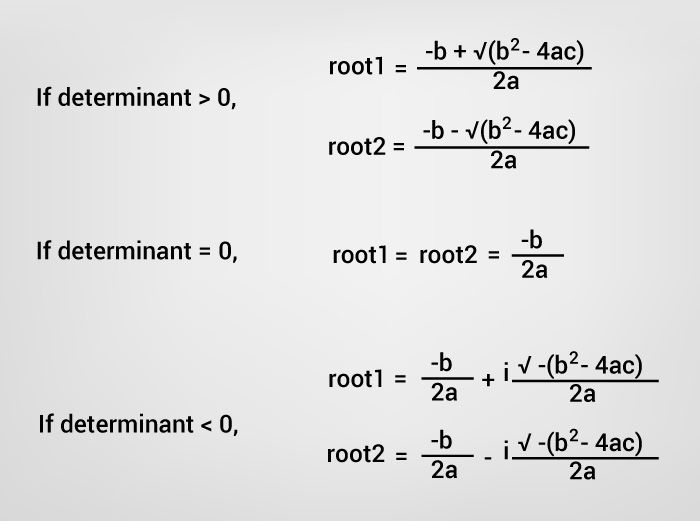
Calculate Root of Quadratic Equation
Example: Roots of a Quadratic Equation
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
float a, b, c, x1, x2, discriminant, realPart, imaginaryPart;
cout << "Enter coefficients a, b and c: ";
cin >> a >> b >> c;
discriminant = b*b - 4*a*c;
if (discriminant > 0) {
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
x2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
cout << "Roots are real and different." << endl;
cout << "x1 = " << x1 << endl;
cout << "x2 = " << x2 << endl;
}
else if (discriminant == 0) {
cout << "Roots are real and same." << endl;
x1 = -b/(2*a);
cout << "x1 = x2 =" << x1 << endl;
}
else {
realPart = -b/(2*a);
imaginaryPart =sqrt(-discriminant)/(2*a);
cout << "Roots are complex and different." << endl;
cout << "x1 = " << realPart << "+" << imaginaryPart << "i" << endl;
cout << "x2 = " << realPart << "-" << imaginaryPart << "i" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter coefficients a, b and c: 4
5
1
Roots are real and different.
x1 = -0.25
x2 = -1
In this program, sqrt() library function is used to find the square root of a number.