Course
Advanced
Measure the Elapsed Time in PythonRepresent enumCreate a Countdown TimerConvert Bytes to a StringIntroduction
Print Hello world!Add Two NumbersFind the Square RootCalculate the Area of a TriangleSolve Quadratic EquationSwap Two VariablesGenerate a Random NumberConvert Kilometers to MilesConvert Celsius To FahrenheitPrint Output Without a NewlineDecision Making and Loops
Check if a Number is Positive, Negative or 0Check if a Number is Odd or EvenCheck Leap YearFind the Largest Among Three NumbersCheck Prime NumberPrint all Prime Numbers in an IntervalFind the Factorial of a NumberDisplay the multiplication TablePrint the Fibonacci sequenceCheck Armstrong NumberFind Armstrong Number in an IntervalFind the Sum of Natural NumbersCreate Pyramid PatternsIterate Over Dictionaries Using for LoopReverse a NumberCompute the Power of a NumberFunctions
Display Powers of 2 Using Anonymous FunctionFind Numbers Divisible by Another NumberConvert Decimal to Binary, Octal and HexadecimalFind ASCII Value of CharacterFind HCF or GCDFind LCMFind the Factors of a NumberMake a Simple CalculatorShuffle Deck of CardsDisplay CalendarDisplay Fibonacci Sequence Using RecursionFind Sum of Natural Numbers Using RecursionFind Factorial of Number Using RecursionConvert Decimal to Binary Using RecursionReturn Multiple Values From a FunctionNative Datatypes
Add Two MatricesTranspose a MatrixMultiply Two MatricesCheck Whether a String is Palindrome or NotRemove Punctuations From a StringSort Words in Alphabetic OrderIllustrate Different Set OperationsCount the Number of Each VowelMerge Two DictionariesAccess Index of a List Using for LoopFlatten a Nested ListSlice ListsSort a Dictionary by ValueCheck If a List is EmptyConcatenate Two ListsCheck if a Key is Already Present in a DictionarySplit a List Into Evenly Sized ChunksParse a String to a Float or IntPrint Colored Text to the TerminalConvert String to DatetimeGet the Last Element of the ListGet a Substring of a StringRandomly Select an Element From the ListCheck If a String Is a Number (Float)Count the Occurrence of an Item in a ListDelete an Element From a DictionaryCreate a Long Multiline StringConvert Two Lists Into a DictionaryTrim Whitespace From a StringIterate Through Two Lists in ParallelCount the Number of Digits Present In a NumberCheck If Two Strings are AnagramCapitalize the First Character of a StringCompute all the Permutation of the StringCount the Number of Occurrence of a Character in StringRemove Duplicate Element From a ListFiles
Merge MailsFind the Size (Resolution) of an ImageFind Hash of FileSafely Create a Nested DirectoryCatch Multiple Exceptions in One LineCopy a FilePython Program Read a File Line by Line Into a ListAppend to a FileExtract Extension From the File NameGet the File Name From the File PathGet Line Count of a FileFind All File with .txt Extension Present Inside a DirectoryGet File Creation and Modification DateGet the Full Path of the Current Working DirectoryCheck the File SizeC++ Program to Find All Roots of a Quadratic Equation
To understand this example, you should have the knowledge of the following C++ programming topics:
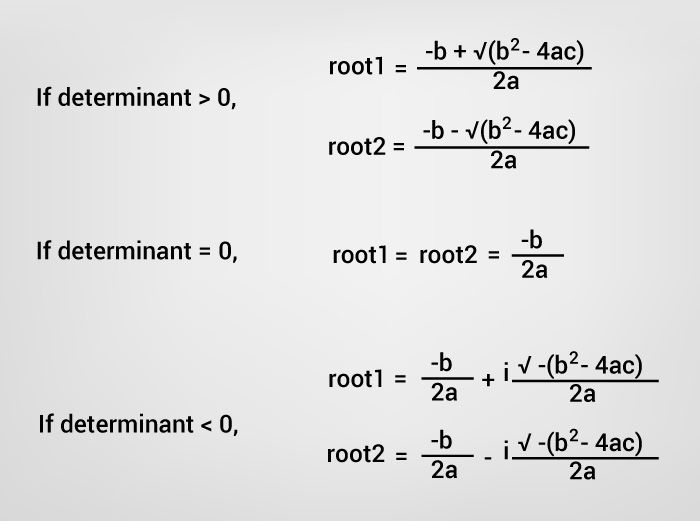
For a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c = 0 (where a, b and c are coefficients), it’s roots is given by following the formula.

Formula to Find Roots of Quadratic Equation
The term b2-4ac is known as the discriminant of a quadratic equation. The discriminant tells the nature of the roots.
- If discriminant is greater than 0, the roots are real and different.
- If discriminant is equal to 0, the roots are real and equal.
- If discriminant is less than 0, the roots are complex and different.
Calculate Root of Quadratic Equation
Example: Roots of a Quadratic Equation
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
float a, b, c, x1, x2, discriminant, realPart, imaginaryPart;
cout << "Enter coefficients a, b and c: ";
cin >> a >> b >> c;
discriminant = b*b - 4*a*c;
if (discriminant > 0) {
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
x2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
cout << "Roots are real and different." << endl;
cout << "x1 = " << x1 << endl;
cout << "x2 = " << x2 << endl;
}
else if (discriminant == 0) {
cout << "Roots are real and same." << endl;
x1 = -b/(2*a);
cout << "x1 = x2 =" << x1 << endl;
}
else {
realPart = -b/(2*a);
imaginaryPart =sqrt(-discriminant)/(2*a);
cout << "Roots are complex and different." << endl;
cout << "x1 = " << realPart << "+" << imaginaryPart << "i" << endl;
cout << "x2 = " << realPart << "-" << imaginaryPart << "i" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter coefficients a, b and c: 4
5
1
Roots are real and different.
x1 = -0.25
x2 = -1
In this program, sqrt() library function is used to find the square root of a number.